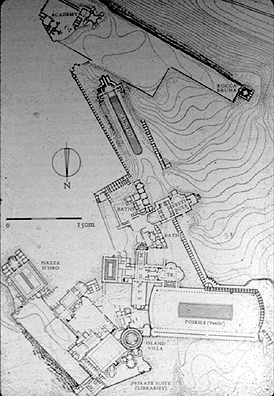
Hadrian’s Villa

1. Locate and label on the diagram all of the following, then explain what sort of area it was and any notable facts about it:
· the Piazza d’Oro [mark in the two notable halls at either end]
· the Greek and Latin libraries
· the Maritime Theatre
· the Poikile
· the Canopus Canal
· the Serapeum
· the Academy
· Hades, the Styx and the Elysian Fields
· the large and smaller Baths
· the Vale of Tempe
2. Read the following statement:
Hadrian was an emperor who travelled widely. He was particularly interested in the Greek culture, including its buildings and philosophy. This villa reflects his nostalgia for places he had visited and in which he had spent time. However, he did set out not to copy places and buildings he had admired elsewhere, but to use them as inspiration for his own designs.
“The new and ingenious craftsmanship, together with traditional features, epitomized the outlook of Hadrian and his epoch.”
[Hanfman]
3. Find some examples of new and ingenious craftsmanship.
4. Find some examples of traditional features. You should incorporate both Classical Greek and typical Roman features.
NB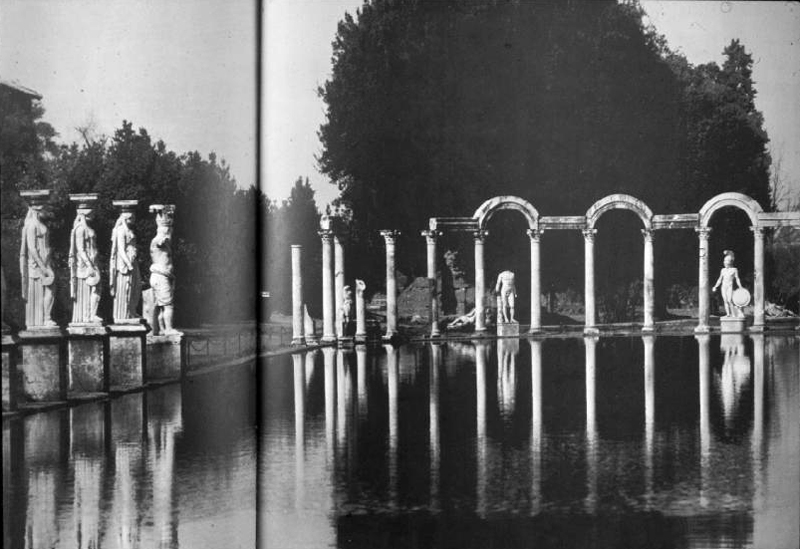
CLASSICAL GREEK FEATURES
· statues
· columns
· colonnaded walkways
TYPICALLY ROMAN ELEMENTS
· the use of concrete in arches and vaults as load-bearing structures
· the use of domes in imperial architecture
· symmetrical arrangement of rooms
· enclosed architectural units
· palatial size and splendour of design and decoration
5. Town planning: Hadrian did not stick to the traditional Roman and Greek regular checkerboard arrangement of his buildings in his villa, which resembles a small town in size. While retaining the typical Roman regularity within each unit, he has a loose asymmetrical arrangement of these units. Describe an area of the villa, which illustrates this.
6. Where is Tivoli?
7. Over what period of time was the Villa built?
8. What materials were used in the buildings on the outside?
9. What materials were used in the buildings on the inside?
10. What interior decorations were originally on the floors?
11. How were the walls decorated?
12. What other decorations were there?
13. How do the names given to the different parts of the villa reflect:
· Hadrian’s travels?
· his increasing age?
· Modern excavations?
14. What similarities are there between Hadrian’s Pantheon and the Piazza d’Oro in his villa?